About Arthur Schopenhauer
March 28, 2017
About Thomas Henry Huxley
March 29, 2017Evolutionary Naturalism
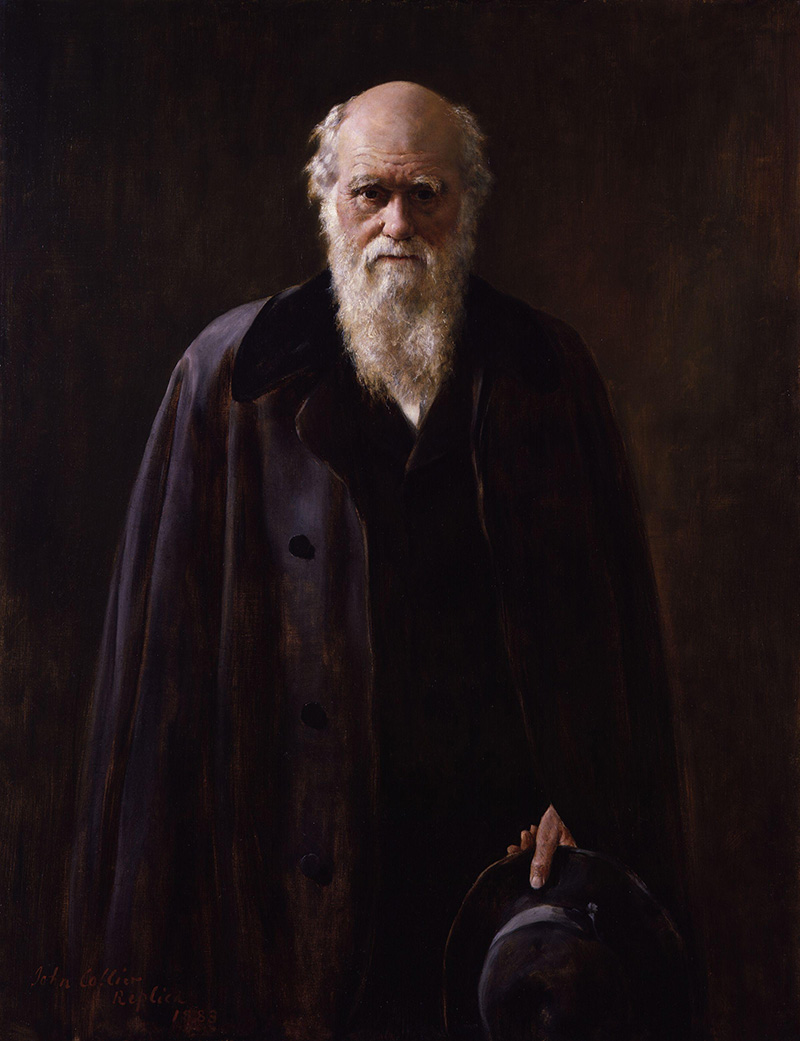
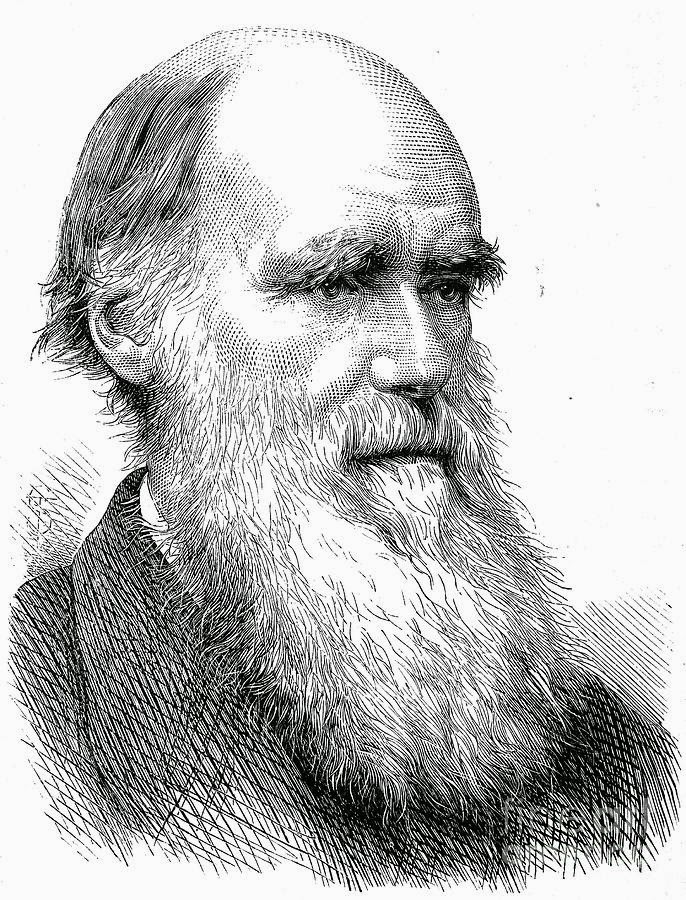
About Charles Robert Darwin
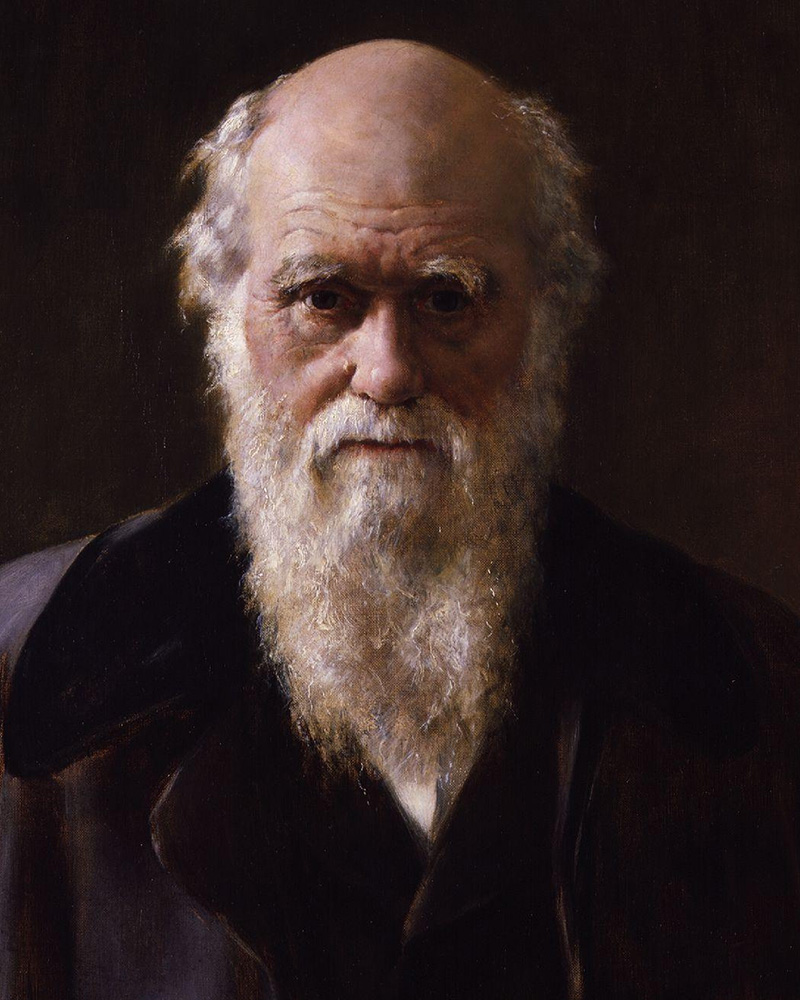

T he word "evolution" in its broadest sense refers to change or growth that occurs in a particular order. Although this broad version of the term would include astronomical evolution and the evolution of computer design, this article focuses on the evolution of biological organisms. That use of the term dates back to the ancient Greeks, but today the word is more often used to refer to Darwin's theory of evolution by natural selection. This theory is sometimes crudely referred to as the theory of "survival of the fittest." It was proposed by Charles Darwin in On the Origin of Species in 1859 and, independently, by Alfred Wallace in 1858—although Wallace, unlike Darwin, said the human soul is not the product of evolution.
Greek and medieval references to "evolution" use it as a descriptive term for a state of nature, in which everything in nature has a certain order or purpose. This is a teleological view of nature. For example, Aristotle classified all living organisms hierarchically in his great scala naturae or Great Chain of Being, with plants at the bottom, moving through lesser animals, and on to humans at the pinnacle of creation, each becoming progressively more perfect in form. It was the medieval philosophers, such as Augustine, who began to incorporate teleological views of nature with religion: God is the designer of all creatures, and everything has a purpose and a place as ordained by Him.
History of Evolution
In current times, to some, the terms "evolution" and "God" may look like unlikely bed fellows (see the discussion on teleology). This is due primarily to today's rejection by biologists of a teleological view of evolution in favor of a more mechanistic one. The process of rejection is commonly considered to have begun with Descartes and to have culminated in Darwin’s theory of evolution by natural selection.
Fundamental to natural selection is the idea of change by common descent. This implies that all living organisms are related to each other; for any two species, if we look back far enough we will find that they are descended from a common ancestor. This is a radically different view than Aristotle’s Great Chain of Being, in which each species is formed individually with its own purpose and place in nature and where no species evolves into a new species. Evolution by natural selection is a purely mechanistic theory of change that does not appeal to any sense of purpose or a designer. There is no foresight or purpose in nature, and there is no implication that one species is more perfect than another. There is only change driven by selection pressures from the environment. Although the modern theory of biological evolution by natural selection is well accepted among professional biologists, there is still controversy about whether natural selection selects for fit genes or fit organisms or fit species.
Evolution by natural selection is a theory about the process of change. Although Darwin's original theory did not specify that genes account for an organism's heritable traits, that is now universally accepted among modern evolutionists. In a given population, natural selection occurs when genetically-based traits that promote survival in one's environment are passed onto future generations and become more frequent in later generations. Organisms develop different survival and reproduction enhancing traits in response to their different environments (with abundance or shortage of food, presence or absence of predators, and so forth) and, given enough time and environmental changes, these small changes can accumulate to form a whole new species. Thus for Darwin there is no sharp distinction between a new variation and a new species. This theory accounts for the diversity of Earth's organisms better than theological design theories or competing scientific theories such as Lamarck's theory that an organism can pass on to its offspring characteristics that it acquired during its lifetime.
Evolution by natural selection works on three principles: variation (within a given generation there will be variation in traits, some that aid survival and reproduction and some that don’t, and some that have a genetic basis and some that don’t); competition (there will be limited resources that individuals must compete for, and traits that aid survival and reproduction will help in competition); and heritability (only traits that aid survival and reproduction and have a genetic basis can passed onto future generations).
Ancient Greek Views
Evolution is not so much a modern discovery as some of its advocates would have us believe. It made its appearance early in Greek philosophy, and maintained its position more or less, with the most diverse modifications, and frequently confused with the idea of emanation, until the close of ancient thought. The Greeks had, it is true, no term exactly equivalent to " evolution"; but when Thales asserts that all things originated from water; when Anaximenes calls air the principle of all things, regarding the subsequent process as a thinning or thickening, they must have considered individual beings and the phenomenal world as, a result of evolution, even if they did not carry the process out in detail. Anaximander is often regarded as a precursor of the modem theory of development. He deduces living beings, in a gradual development, from moisture under the influence of warmth, and suggests the view that men originated from animals of another sort, since if they had come into existence as human beings, needing fostering care for a long time, they would not have been able to maintain their existence. In Empedocles, as in Epicurus and Lucretius, who follow in Hs footsteps, there are rudimentary suggestions of the Darwinian theory in its broader sense; and here too, as with Darwin, the mechanical principle comes in; the process is adapted to a certain end by a sort of natural selection, without regarding nature as deliberately forming its results for these ends.
If the mechanical view is to be found in these philosophers, the teleological occurs in Heraclitus, who conceives the process as a rational development, in accordance with the Logos and names steps of the process, as from igneous air to water, and thence to earth. The Stoics followed Heraclitus in the main lines of their physics. The primal principle is, as with him, igneous air. only that this is named God by them with much greater definiteness. The Godhead has life in itself, and develops into the universe, differentiating primarily into two kinds of elements the finer or active, and the coarser or passive. Formation or development goes on continuously, under the impulse of the formative principle, by whatever name it is known, until all is once more dissolved by the ekpyrosis into the fundamental principle, and the whole process begins over again. Their conception of the process as analogous to the development of the seed finds special expression in their term of logos spermatikos. In one point the Stoics differ essentially from Heraclitus. With them the whole process is accomplished according to certain ends indwelling in the Godhead, which is a provident, careful intelligence, while no providence is assumed in Heraclitus.
Empedocles asserts definitely that the sphairos, as the full reconciliation of opposites, is opposed, as the superior, to the individual beings brought into existence by hatred, which are then once more united by love to the primal essence, the interchange of world-periods thus continuing indefinitely. Development is to be found also in the atomistic philosopher Democritus; in a purely mechanical manner without any purpose, bodies come into existence out of atoms, and ultimately entire worlds appear and disappear from and to eternity. Like his predecessors, Deinocritus, deduces organic beings from what is inorganic-moist earth or slime.
Development, as well as the process of becoming, in general, was denied by the Eleatic philosophers. Their doctrine, diametrically opposed to the older thoroughgoing evolutionism, had its influence in determining the acceptance of unchangeable ideas, or forms, by Plato and Aristotle. Though Plato reproduces the doctrine of Heraclitus as to the flux of all things in the phenomenal world, he denies any continuous change in the world of ideas. Change is permanent only in so far as the eternal forms stamp themselves upon individual objects. Though this, as a rule, takes place but imperfectly, the stubborn mass is so far affected that all works out as far as possible for the best. The demiurge willed that all should become as far as possible like himself; and so the world finally becomes beautiful and perfect. Here we have a development, though the principle which has the most real existence does not change; the forms, or archetypal ideas, remain eternally what they are.
In Aristotle also the forms are the real existences, working in matter but eternally remaining the same, at once the motive cause and the effectual end of all things. Here the idea of evolution is clearer than in Plato, especially for the physical world, which is wholly dominated by purpose. The transition from lifeless to living matter is a gradual one, so that the dividing-line between them is scarcely perceptible. Next to lifeless matter comes the vegetable kingdom, which seems, compared with the inorganic, to have life, but appears lifeless compared with the organic. The transition from plants to animals is again a gradual one. The lowest organisms originate from the primeval slime, or from animal differentiation; there is a continual progression from simple, undeveloped types to the higher and more perfect. As the highest stage, the end and aim of the whole process, man appears; all lower forms are merely unsuccessful attempts to produce him. The ape is a transitional stage between man and other viviparous animals. If development has so important a work in Aristotle's physics, it is not less important in his metaphysics. The whole transition from potentiality to actuality (from dynamis toentelecheia) is nothing but a transition from the lower to the higher, everything striving to assimilate itself to the absolutely perfect, to the Divine. Thus Aristotle, like Plato, regards the entire order of the universe as a sort of deification. But the part played in the development by the Godhead, the absolutely immaterial form, is less than that of the forms which operate in matter, since, being already everything,, it is incapable of becoming anything else. Thus Aristotle, despite his evolutionistic notions, does not take the view of a thoroughgoing evolutionist as regards the universe; nor do the Neoplatonists, whose highest principle remains wholly unchanged, though all things emanate from it.
Medieval Views
The idea of evolution was not particularly dominant in patristic and scholastic theology and philosophy, both on account of the dualism which runs through them as an echo of Plato and Aristotle, and on account of the generally accepted Christian theory of creation. However, evolution is not generally denied; and with Augustine (De civitate dei, xv. 1) it is taken as the basis for a philosophy of history. Erigena and some of his followers seem to teach a sort of evolution. The issue of finite beings from God is called analysis or resolution in contrast to the reverse or deification the return to God, who once more assimilates all things. God himself, although denominated the beginning, middle, and end, all in all remains unmixed in his own essence, transcendent though immanent in the world. The teaching of. Nicholas of Cusa is similar to Erigena's, though a certain amount of Pythagoreanism comes in here. The world exhibits explicitly what the Godhead implicitly contains; the world is an animated, ordered whole, in which God is everywhere present. Since God embraces all things in himself, he unites all opposites: he is the complicatio omnium contradictoriorum. The idea of evolution thus appears in Nicholas in a rather pantheistic form, but it is not developed.
In spite of some obscurities in his conception of the world Giordano Bruno is a little clearer. According to him God is the immanent first cause in the universe; there is no difference between matter and form; matter, which includes in itself forms and ends, is the source of all becoming and of all actuality. The infinite ether which fills infinite space conceals within itself the nucleus of all things, and they proceed from it according to determinate laws, yet in a teleological manner. Thus the worlds originate not by an arbitrary act, but by an inner necessity of the divine nature. They are natura naturata, as distinguished from the operative nature of God, natitra naturans, which is present in all thin-S as the being- of all that is, the beauty of all that is fair. As in the Stoic teaching, with which Bruno's philosophy has much in common, the conception of evolution comes out clearly both for physics and metaphysics.
In Modern Philosophy
Leibniz attempted to reconcile the mechanical-physical and the teleological views, after Descartes, in his Principia philosophitce, excluding all purpose, had explained nature both lifeless and living, as mere mechanism. It is right, however, to point out that Descartes had a metaphysics above his physics, in which the conception of God took an important place, and that thus the mechanical notion of evolution did not really include everything. In Leibnitz the principles of mechanics and physics are dependent upon the direction of a supreme intelligence, without which they would be inexplicable to us. Only by such a preliminary assumption are we able to recognize that one ordered thing follows upon another continuously. It is in this sense that the law of continuity is to be understood, which is of such great importance in Leibnitz. At bottom it is the same as the law of ordered development. The genera of all beings follow continuously one upon another, and between the main classes, as between animals and vegetables, there must be a continuous sequence of intermediate beings. Here again, however, evolution is not taught in its most thorough form, since the divine monad, of God, does not come into the world but transcends it.
Among the German philosophers of the eighteenth century Herder must be mentioned first of the pioneers of modern evolutionism. He lays down the doctrine of a continuous development in the unity of nature from inorganic to organic, from the stone to the plant, from the plant to the animal, and from the animal to man. As nature develops according to fixed laws and natural conditions, so does history, which is only a continuation of the process of nature. Both nature and history labor to educate man in perfect humanity; but as this is seldom attained, a future life is suggested. Lessing had dwelt on the education of the human race as a development to the higher and more perfect. It is only recently that the significance of Herder, in regard to the conception and treatment of historic development, has been adequately recognized. Goethe also followed out the idea of evolution in his zoological and botanical investigations, with his theory of the metamorphosis of plants and his endeavor to discover unity in different organisms.
In German Idealism
Kant is also often mentioned as having been an early teacher of the modern theory of descent. It is true he considers the analogy of the forms which he finds in various classes of organisms a ground for supposing that they may have come originally from a common source. He calls the hypothesis that specifically different being have originated one from the other "a daring adventure of the reason." But he entertains the thought that in a later epoch "an orang-outang or a chimpanzee may develop the organs which serve for walking, grasping objects, and speaking-in short, that lie may evolve the structure of man, with an organ for the use of reason, which shall gradually develop itself by social culture." Here, indeed, important ideas of Darwin were anticipated; but Kant's critical system was such that development could have no predominant place in it.
The idea of evolution came out more strongly in his German idealistic successors, especially in Schelling, who regarded nature as a preliminary stage to mind, and the process of physical development as continuing in history. The unconscious productions of nature are only unsuccessful attempts to reflect itself; lifeless nature is an immature intelligence, so that in its phenomena an intelligent character appears only unconsciously. Its highest aim, that, of becoming an object to itself, is only attained in the highest and last reflection-in man, or in what we call reason, through which for the first time nature returns perfectly upon itself. All stages of nature are connected by a common life, and show in their development a conclusive unity. The course of history as a whole must be conceived as offering a gradually progressive revelation of the Absolute. For this he names three periods-that of fate, that of nature, and that of providence, of which we are now in the second. Schelling's followers carried the idea of development somewhat further than their master. This is true especially of Oken, who conceives natural science as the science of the eternal transformation of God into the world, of the dissolution of the Absolute into plurality, and of its continuous further operation in this plurality. The development is continued through the vegetable and animal kingdoms up to man, who in his art and science and polity completely establishes the will of nature. Oken, it is true, conceived man as the sole object of all animal development, so that the lower stages are only abortive attempts to produce him-a theory afterward controverted by Ernst von Baer and Cuvier, the former of whom, standing somewhat in opposition to Darwin, is of great interest to the student of the history of the theory of evolution.
Some evolutionistic ideas are found in Krause and Schleiermacher; but Hegel, with his absolute idealism, is a more notable representative of them. In his system philosophy is the science of the Absolute, of the absolute reason developing or unfolding itself. Reason develops itself first in the abstract element of thought, then expresses itself externally in nature, and finally returns from this externalization into itself in mind. As Heraclitus had taught eternal becoming, so Hegel, who avowedly accepted all the propositions of the Ephesian philosopher in his logic, taught eternal proceeding. The difference between the Greek and the German was that the former believed in the flux of matter, of fire transmuting itself by degrees into all things, and in nature as the sole existence, outside of which there was nothing; while the latter conceived the abstract idea or reason as that which really is or becomes, and nature as only a necessary but transient phase in the process of development. With Heraclitus evolution meant the return of all things into the primal principle followed by a new world-development; with Hegel it was an eternal process of thought, giving no answer to the question as to the end of historical development.
Darwin's View
While Heraclitus had laid down his doctrine of eternal becoming rather by intuition than on the ground of experience, and the entire evolutionary process of Hegel had been expressly conceived as based on pure thought, Darwin's and Wallace's epoch-making doctrine rested upon a vast mass of ascertained facts. He was, of course, not the first to lay down the origin of species one from another as a formal doctrine. Besides those predecessors of his to whom allusion has already been made, two others may be mentioned here: his grandfather, Erasmus Darwin, who emphasized organic variability; and still more Lamarck, who denied the immutability of species and forms, and claimed to have demonstrated by observation the gradual development of the animal kingdom. What is new in Charles Darwin is not his theory of descent, but its confirmation by the theory of natural selection and the survival of the fittest in the struggle for existence. Thus a result is brought about which corresponds as far as possible to a rational end in a purely mechanical process, without any cooperation of teleological principles, without any innate tendency in the organisms to proceed to a higher stage. This theory postulates in the later organisms deviations from the earlier ones; and that these deviations, in so far as they are improvements, perpetuate themselves and become generic marks of differentiation. This, however, imports a difficulty, since the origin of the first of these deviations is inexplicable. The differentia of mankind, whom Darwin, led by the force of analogy, deduces from a species of apes, consists in intellect and moral qualities, but comes into existence only by degrees. The moral sensibilities develop from the original social impulse innate in man; this impulse is an effort to secure not so much individual happiness as the general welfare.
It would be impossible to name here all those who, in different countries, have followed in Darwin's footsteps, first in the biological field and then in those of psychology, ethics, sociology, and religion. They have carried his teaching further in several directions, modifying it to some extent and making it fruitful, while positivism has not seldom come into alliance with it. In Germany Ernst Haeckel must be mentioned with his biogenetic law, according to which the development of the individual is an epitome of the history of the race, and with his less securely grounded notion of the world-ether as a creative deity. In France Alfred Fouillee worked out a theory of idea-forces, a combination of Platonic idealism with English (though not specifically Darwinian) evolutionism. Marie-Jean Guyau understood by evolution a life led according to the fundamental law that the most intensive life is also the most extensive. He develops his ethics altogether from the facts of the social existence of mankind, and his religion is a universal sociomorphism, the feeling of the unity of man with the entire cosmos.
Spencer's View
The most careful and thorough development of the whole system took place in England. For a long time it was represented principally by the work of Herbert Spencer, who had come out for the principle of evolution even before the publication of Darwin's Origin of Species. He carries the idea through the whole range of philosophy in his great System of Synthetic Philosophy and undertakes to show that development is the highest law of all nature, not merely of the organic. As the foundation of ill that exists, though itself unknowable and only revealing itself in material and mental forms, he places a power, the Absolute, of which we have but an indefinite conception. The individual processes of the world of phenomena are classed under the head of evolution, or extension of movement, with which integration of matter, union into a single whole, is connected, and dissolution or absorption of movement, which includes disintegration of matter, the breaking of connection. Both processes go on simultaneously, and include the history of every existence which we can perceive. In the course of their development the organisms incorporate matter with themselves; the plant grows by taking into itself elements which have previously existed in the form of gases, and the animal by assimilating elements found in plants and in other animals. The same sort of integration is observed in social organisms, as when nomadic families unite into a tribe, or subjects under a prince, and princes under a king. In like manner integration is evident in the development of language, of art, and of science, especially philosophy. But as the individuals unite into a whole, a strongly marked differentiation goes on at the same time, as in the distinction between the surface and the interior of the earth, or between various climates. Natural selection is not considered necessary to account for varying species, but gradual conditions of life create them. The aim of the development is to show a condition of perfect balance in the whole; when this is attained, the development, in virtue of the continuous operation of external powers, passes into dissolution. Those epochs of development and of dissolution follow alternately upon each other. This view of Spencer suggests the hodos ano and hodos kato of Heraclitus, and his flowing back of individual things into the primal principle.
Similar principles are carried out not only for organic phenomena but also for mental and social; and on the basis of the theory of evolution a remarkable combination of intuitionism and empiricism is achieved. In his principles of sociology Spencer lays down the laws of hyperorganic evolution, and gives the various stages of human customs and especially of religious ideas, deducing all religion much too one-sidedly from ancestor-worship. The belief in an immortal " second self " is explained by such phenomena as shadows and echoes. The notion of gods is suppose to arise from the idea of a ghostly life after death. In his Principles of Ethics he attempts a similar compromise between intuitionism and empiricism, deducing the consciousness of duty from innumerable accumulated experiences. The compelling element in moral actions, originally arising from fear of religious, civil, or social punishment, disappears with the development of true morality. There is no permanent opposition between egoism and altruism, but the latter develops simultaneously with the former.
Spencer's ethical principles were fruitfully modified, especially by Sir Leslie Stephen and S. Alexander, though with constant adherence to the idea of development. While the doctrine of evolution in Huxley and Tyndall is associated with agnosticism, and thus freed from all connection with metaphysics, as indeed was the case with Spencer, in spite of his recognition of the Absolute as the necessary basis for religion and for thought, in another direction an attempt was made to combine evolutionism closely with a metaphysics in which the idea of God was prominent. Thus the evolution theory of Clifford and Romanes led them to a thoroughgoing monism, and that of J. M. F. Schiller to pluralism. According to the last-named a personal deity, limited in power, exists side by side with a multitude of intellectual beings, who existed before the formation of the world in a chaotic state as absolutely isolated individuals. The process of world formation begins with the decision of the divine Spirit to bring a harmony of the cosmos out of these many existences. Though Spencer's influence in philosophical development was not so great in Germany as in England, the idea of development has continued in recent years to exert no little power. Space forbids more than a mention of Lotze's teleological idealism; Von Harttmann's absolute monism, in which the goal of the teleological development of the universe is the reversion of the will into not-willing; Wundt's metaphysics of the will, according to which the world is a development, an eternal becoming, in which nature is a preliminary stage to mind; and Nietzsche's individualism, the final point of which is the development of the superman.